| About College | ||
| Academic Programmes | ||
| Infrastructure | ||
| Mandate | ||
| Faculty | ||
| Co-Curricular Activities | ||
| Research Activities and Achievements | ||
| Extension Activities and Achievements | ||
| Publications | ||
| Contact Information |
About College
Being a state of horticulture, the B.Sc. (Horticulture) four years degree programme has been implemented by the Maharashtra state Government from July 1984 with 20 intake capacity (16 male + 4 female). Up to 2001, this programme was run under the establishment of College of Agriculture, Akola with one Professor (Hort.), two post of Associate Professor (Hort.) and six Assistant professor (three from Hort. and three allied discipline).
Later on vide Univ. order No.BBE/0426/ (VIII) 3, dated 25th January, 2001, the full fledged independent college of horticulture has been started by filling the additional post through redeployment. Now, from 25th January, 2001 this college functioning independently with the intake capacity of 36 students plus 15 % ICAR nominated students.
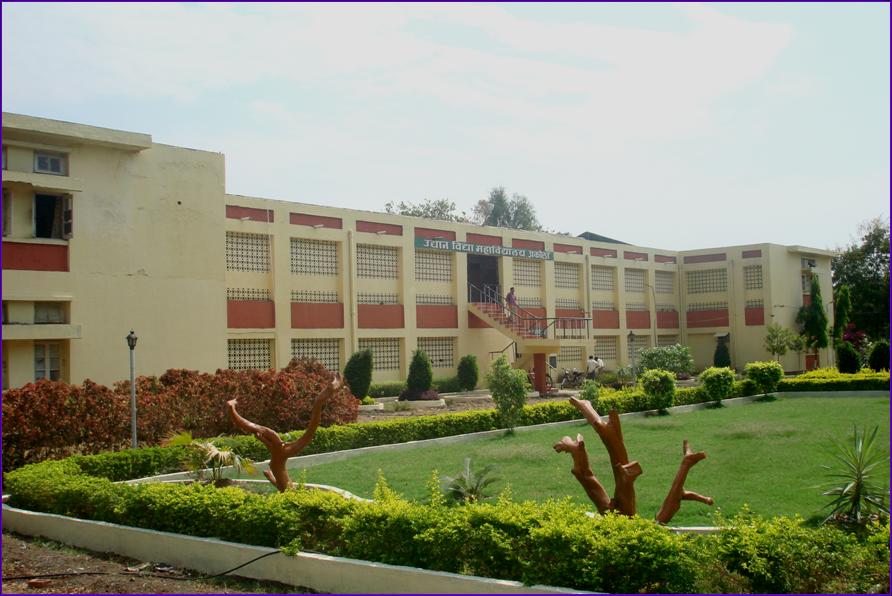

College of Horticulture, Akola
Sections
The Dean, Faculty of Agriculture is the controlling officer of the College. The Associate Dean, College of Horticulture is head of the office. The teaching and non-teaching staffs are working under Associate Dean. The Assistant Registrar is the in-charge of Account section. There are nine divisions in this College as given below:
- Fruit Science
- Vegetable Science
- Floriculture and landscape gardening
- Post Harvest Technology
- General Horticulture
- Nursery management
- Plant Protection of Horticultural Crops
- Agril. and allied discipline
- Basic Science
Academic Programmes
|
Degree Programme
|
Duration
|
|
B.Sc. Horticulture
|
04
|
Infrastructure Facilities
Since the inception of college good infrastructural facilities for imparting undergraduate programme has been developed. The infrastructural development at this college is from the funds made available from university grants, ICAR grants and various funding agencies in the form of projects.
Infrastructural facilities available with the College.
|
Sr. No. |
Facilities |
Nos. |
|---|---|---|
|
1. |
Building |
03 |
|
2. |
Class Rooms |
02 |
|
3. |
Laboratory |
06 |
|
4. |
Boys Hostel |
01 |
|
5. |
Girls Hostel (Common with Agril. Girls) |
01 |
|
6. |
Land / Field |
31.00 ha. |
|
7. |
Mini Bus (16 seater) |
01 |
|
8. |
Car |
01 |
|
9. |
Tractor with trolley |
01 |
Classroom ,computer laboratory and seminar hall
The university allotted the present building for establishment of college of horticulture, which was Post Graduate Institute earlier. Since the inception of independent college from 25th January 2001 and subsequent induction of academic staff and ministerial staff, the existing building has sufficient to accommodate the staff. However, laboratory facility was lacking and seven independent well-equipped laboratories are developed. Presently the college of horticulture is holding two classrooms, seven laboratories and one computer lab. To conduct the seminar and other activities, one fully equipped seminar hall is available.
Transport facilities
The college is having one 16 seater mini bus pooled from the university vehicle fleets. This vehicle is used for field visit to university farm and cultivators field near by the university campus for practical purpose.
Specialized laboratories/ facilities
The college has developed good laboratories/ facilities for imparting teaching like
- Fruit Science
- Vegetable Science
- Floriculture
- Post Harvest Technology
- Plant Protection
- Agril Extension
- Poly house and Net House
- Computer center
- Nursery Unit
 |
 |
|
| Computer Laboratory | Seminar Hall |
Mandate
-
To cater the need of future research based horticulture development and fulfill demand of the specialized technical personnel of this region.
- To provide scientific manpower in the field of horticulture.
- To undertake the basic research in the field of horticulture for optimum production of horticulture produce.
-
To provide the balance diet through various horticultural crop to make Indian more healthy.
Co-Curricular Activities
-
Received one prize in the flower show organized by Vidarbha Rose Society, Nagpur (2003).
- Staff participation in refresher courses to update their know-how for effective teaching and research
- Received 12 trophy/award in flower show organized by Akola Garden Club, Akola (2001-06).
- City garden of this College Received “Best Institutional Garden Trophy” in Flower show organized by Akola Garden Club, Akola during 2004-05, 2005-06, 2006-07 and 2007-08
-
Student participation in social event like Youth Festival, NSS, NCC, etc.
Student Achievements
Students of this college have shown a tremendous incline curve in the success of securing the seats in the competitive examinations of ‘Junior Research Fellow’ for their academic development. Apart from this, the Maharashtra Council of Agricultural Research and Education, Pune has introduced the Combined Entrance Examination for Post Graduate Courses from 2006-07. The students from this college are qualified for post graduate admission through Combined Entrance Examination-2006-07.
Nos. of students securing ICAR’s JRF
|
Year
|
JRF
|
|---|---|
|
2003-2004
|
05
|
|
2004-2005
|
07
|
|
2005-2006
|
07
|
|
2006-2007
|
09
|
|
2007-2008
|
03
|
|
2008-2009
|
01
|
|
2009-2010
|
04
|
|
2010-2011
|
03
|
Significant achievement of the student (2003-2008)
The student of this college participated in various activities and records the significant achievement.
-
In ICAR entrance examination, Mr. Mahesh Kumar secured 2nd rank at national level and opt admission in IARI, New Delhi (2004-2005)
- Mr. Pranav Kulkarni is selected to represent University ‘Avishkar’ Research Festival during 2006-07 and 2007-08 at Nagpur and Mumbai respectively. Mr.Pranav Kulkarni got second prize in the Inter University ‘Avishkar’ Research Festival during 2006-07 held at Nagpur.
- Mr. Narendra Meena got admission in Central Food Research Technology Institute, Mysore for Post Graduate Studies through entrance examination.
- Nine and Five students have been selected through campus interview as a “Recovery Officer” in the State Bank of India and IDBI respectively
- In ICAR entrance examination, Mr. Bharat Singh Hada secured 4th rank at national level in 2008-09 and other seven students qualify the ICAR entrance examination.
-
During 2009-10, in ICAR entrance examination, Mr. Vijay Kakade, secured 1st rank at national level in general category AND Mr. Awachare secured 1st rank at national level in scheduled caste category.
Students placement cell
The student’s placement cell is formed at college level for the guidance and proper channeling the horticulture graduates in the field of horticulture and allied fields. The core activities of this cell are:
- To guide the students for employment in various fields by conducting campus interviews.
- Keeping liaisons with the state department as well as private sectors.
- Motivating and guiding students for their higher studies for National and International Institutes.
Education Tour
 |
 |
|
| Educational Tour – Visit to IIHR, Bangalore | Visit to NOGA, Nagpur |
Research Activities and Achievements
In addition to the teaching, academic staff members are actively involved in research activities. The academic staff members publish regularly research and review papers in National and International journals regularly and they are also participated in National and international conference, seminars and symposium.
The academic staff members are conducted the following research projects and presented the report in the Research Review Committee meeting.
Research projects in operation at college of horticulture:
- Survey, collection, maintenance and evaluation of elite types of mango.
- Survey, collection, maintenance and evaluation of elite types of custard apple.
- Effect of GA3 and chemicals on seed germination of cincona (Acacia rigta).
- Propagation studies in jamun.
- Crop improvement studies in cluster bean.
- Crop improvement studies in dolichos bean.
- Crop improvement in lima bean.
- Crop improvement in bottle gourd.
- Crop improvement in sponge gourd.
- Crop improvement in bitter gourd.
- Crop improvement in ridge gourd.
- Crop improvement in perennial vegetable- drumstick.
- Crop improvement in amaranthus
- Crop improvement in green fruited brinjal
In addition to the college activity, following units are working under our esteem college.
- Fruit Research Unit.
- Commercial Fruit Nursery.
- Parks & Garden Unit.
- City Garden
- Mali Training
Extension Activities and Achievements
In addition to teaching and research the teachers of college have rendered advisory services to farmers, fruit growers, State Agriculture Department and NGO’s by visiting their fields and answering quarries raised by them through mail /post. The academic staff members are also working as Subject Matter Specialist with extension wing of the State department of Agriculture. Some academic staff members render the services for Kisan Call Centre at ATIC, Dr.Panjabrao Deshmukh Krishi Vidyapeeth, Akola. The teachers of this College are also actively involved in dissemination of technical information through extension publication, radio talks, and TV programmes. The teachers of this college are also actively involved in Krishi melawa, Shivar Pheri, Agriculture exhibitions and field visits
Extension activities carried out during 2003-09:
|
Sr. No.
|
Particulars |
Nos.
|
|---|---|---|
|
1.
|
Popular articles |
188
|
|
2.
|
Booklets/ Leaflets |
12
|
|
3.
|
Radio talks |
30
|
|
4.
|
T.V. talks |
08
|
|
5.
|
Advise to the farmers |
3452
|
Training programme under National Horticulture Mission:
Following training programme are sanctioned by the government of Maharashtra under National Horticulture Mission and same will organized in the month of September, 2006 and January, 2007.
|
Sr. No.
|
Name of Training |
No. of Participant
|
Duration
|
Fund Sanctioned
(Rs Lakh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1.
|
Officer’s Training Programme on Dry land Fruit Crops
|
25
|
5 days
|
2.50
|
|
2.
|
Officer’s Training Programme on Nursery Management
|
25
|
15 days
|
5.00
|
|
3.
|
Officer’s Training Programme on Dry land Fruit Crops
|
50
|
5 days
|
2.50
|
|
4.
|
Officer’s Training Programme on Nursery Management
|
50
|
5 days
|
2.50
|
|
5.
|
Officer’s Training Programme on Nagpur mandarin and Kagzi lime production technology
|
25
|
1 day
|
0.25
|
Publications

Contact Information
Dr. Prakash K. Nagre
Associate Dean
College of Horticulture,
Dr. PDKV, Akola

 December 30th, 2013
December 30th, 2013 

















































 ,
,


































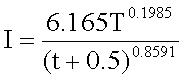
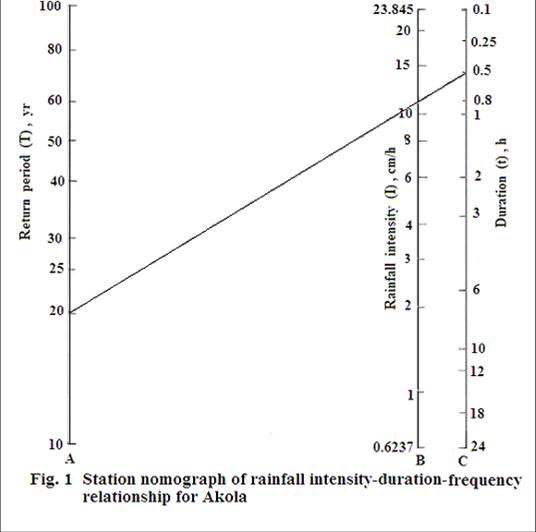
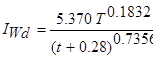

 ; For Buldhana,
; For Buldhana, 
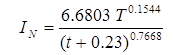 ; For Chandrapur,
; For Chandrapur, 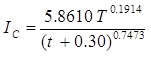
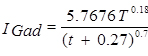 ; For Gondia,
; For Gondia, 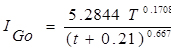












 Krishikosh Repository
Krishikosh Repository